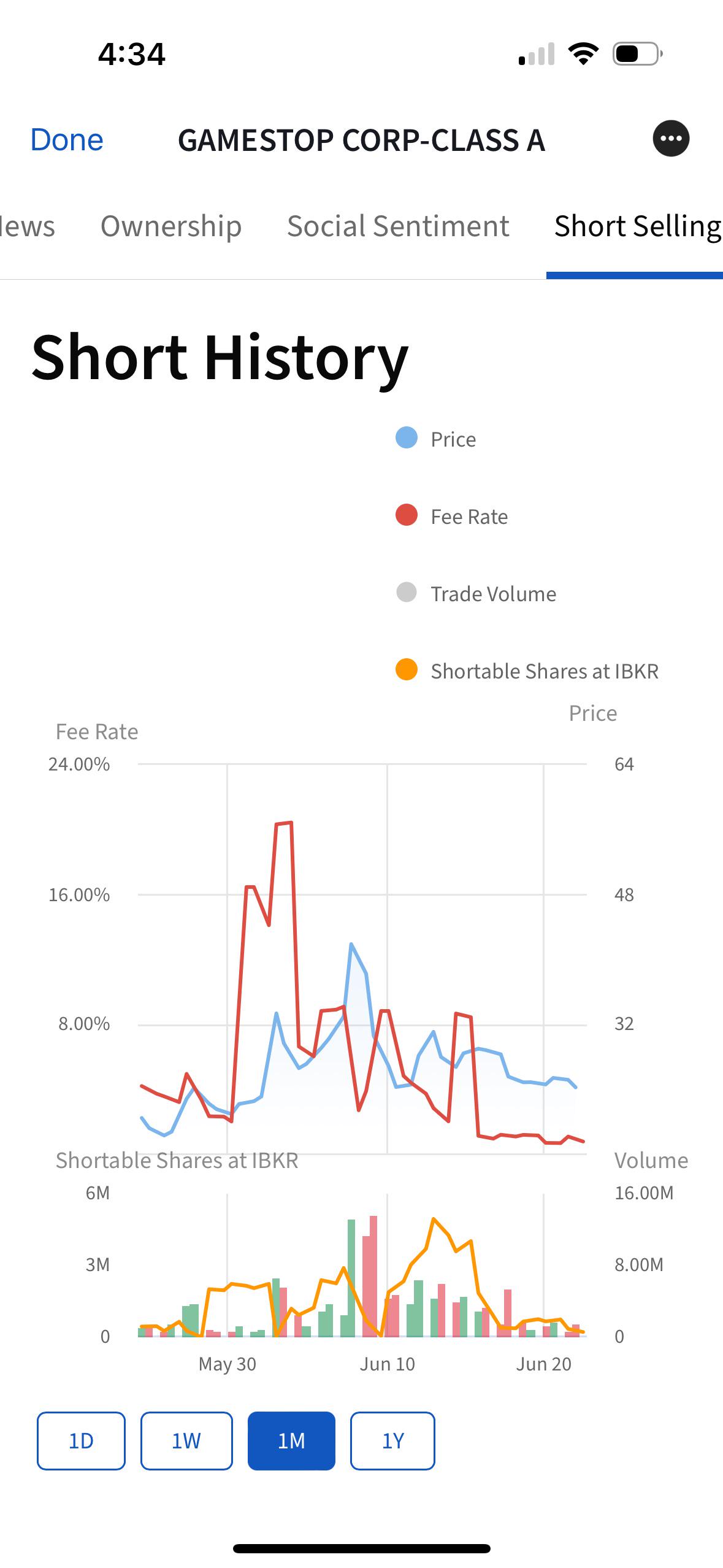
The GameStop (GME) stock saga has captured the attention of investors and the general public alike. A pivotal aspect of this phenomenon is the cost to borrow GME stock, a critical factor for those involved in short selling. Understanding this cost is essential for traders who wish to leverage potential market movements for profit. The cost to borrow GME stock is influenced by multiple factors, including market demand, stock availability, and overall market conditions. This fee can significantly impact an investor's decision to short sell, making it a crucial element in their trading strategy.
For many, the allure of short selling GME stock stems from its volatile price movements and heightened media attention. However, the cost to borrow this stock is not to be underestimated. As the demand to short sell increases, so does the cost, creating a dynamic environment where costs can fluctuate rapidly. This can lead to significant expenses for traders, particularly those who do not factor in these costs when planning their trades. Therefore, understanding the intricacies of the cost to borrow GME stock is paramount for any investor looking to engage in this market.
The GME stock cost to borrow has become a hot topic among traders and financial analysts, as it plays a critical role in the broader market dynamics surrounding GameStop. As market conditions change and new information becomes available, the cost to borrow can vary significantly. Investors must stay informed and adapt their strategies accordingly to navigate this complex and ever-changing landscape. By gaining a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the cost to borrow GME stock, traders can make more informed decisions and potentially capitalize on market opportunities.
Table of Contents
- What is the GME Stock Cost to Borrow?
- Why Does the Cost to Borrow Matter?
- How is the Cost to Borrow Calculated?
- Factors Influencing GME Stock Cost to Borrow
- How Does Market Demand Affect the Cost?
- Can the Cost to Borrow Affect Stock Prices?
- How Do Interest Rates Impact Borrowing Costs?
- Strategies for Managing Borrowing Costs
- What are the Risks Involved in Borrowing GME Stock?
- Case Studies: Borrowing Costs in Action
- How to Stay Updated on GME Stock Borrowing Costs?
- Comparing Borrowing Costs Across Different Stocks
- What Tools Can Help Analyze Borrowing Costs?
- How to Predict Future Borrowing Costs?
- The Future of GME Stock Cost to Borrow
What is the GME Stock Cost to Borrow?
The GME stock cost to borrow refers to the fee that traders must pay to borrow shares of GameStop for short selling purposes. This cost is an integral part of the short selling process, as traders must first borrow shares from a broker before they can sell them on the open market. The borrowing cost is usually expressed as an annualized percentage rate, which varies based on market conditions and the availability of shares. Understanding this cost is crucial for traders looking to engage in short selling, as it can significantly impact potential profits and losses.
Why Does the Cost to Borrow Matter?
The cost to borrow plays a significant role in short selling because it directly affects the profitability of the trade. When borrowing costs are high, traders must generate more profit from the price decline of the stock to cover the expenses. Conversely, lower borrowing costs mean that traders can achieve profitability with smaller price movements. Therefore, understanding the cost to borrow is essential for traders to make informed decisions and manage their risk effectively. Moreover, the cost to borrow can also signal market sentiment, as higher costs may indicate increased demand for short selling and potential downward pressure on the stock price.
How is the Cost to Borrow Calculated?
The calculation of the cost to borrow GME stock involves several factors, including the stock's availability, market demand, and the broker's lending rates. The borrowing cost is typically calculated as an annualized percentage rate, which is applied to the total value of the borrowed shares. This rate can fluctuate based on changes in supply and demand dynamics in the market. Brokers may also impose additional fees or charges, which can further affect the overall cost to borrow. Traders should be aware of these factors and consider them when planning their short selling strategies.
Factors Influencing GME Stock Cost to Borrow
The cost to borrow GME stock is influenced by various factors, including:
- Market Demand: Higher demand for short selling can drive up borrowing costs, as brokers may have limited shares available for lending.
- Stock Availability: Limited availability of shares can lead to higher borrowing costs due to increased competition among traders.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can affect borrowing costs, as brokers may adjust their lending rates accordingly.
- Market Conditions: Volatility and overall market sentiment can impact the cost to borrow, as traders adjust their strategies based on perceived risks and opportunities.
How Does Market Demand Affect the Cost?
Market demand plays a crucial role in determining the cost to borrow GME stock. When demand for short selling increases, brokers may have fewer shares available for lending, leading to higher borrowing costs. This increased demand can be driven by various factors, such as negative news or market sentiment suggesting a potential decline in the stock price. Traders should monitor market demand closely, as it can provide valuable insights into potential price movements and help them make informed decisions about their trading strategies.
Can the Cost to Borrow Affect Stock Prices?
The cost to borrow can have an indirect impact on stock prices, as it influences the behavior of short sellers. When borrowing costs are high, traders may be discouraged from short selling, reducing downward pressure on the stock price. Conversely, lower borrowing costs can encourage more short selling, potentially leading to increased selling pressure and a decline in the stock price. Additionally, high borrowing costs can signal increased market interest in short selling, which may affect investor sentiment and contribute to price volatility.
How Do Interest Rates Impact Borrowing Costs?
Interest rates are a key factor in determining borrowing costs, as brokers often adjust their lending rates based on prevailing interest rates in the market. When interest rates are high, borrowing costs may increase, making short selling more expensive for traders. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to reduced borrowing costs, providing traders with more favorable conditions for short selling. Traders should keep an eye on interest rate trends and consider their potential impact on borrowing costs when planning their trading strategies.
Strategies for Managing Borrowing Costs
To effectively manage borrowing costs, traders can implement various strategies, such as:
- Monitoring Market Conditions: Stay informed about market trends and changes in demand for short selling to anticipate potential shifts in borrowing costs.
- Choosing the Right Broker: Select a broker with competitive lending rates and transparent fee structures to minimize borrowing costs.
- Optimizing Position Size: Adjust the size of short positions to manage borrowing costs and mitigate potential losses.
- Utilizing Hedging Strategies: Implement hedging strategies to offset borrowing costs and reduce overall risk exposure.
What are the Risks Involved in Borrowing GME Stock?
Borrowing GME stock for short selling involves several risks, including:
- Potential Unlimited Losses: Short selling exposes traders to unlimited losses if the stock price rises instead of falling.
- Margin Calls: Traders may face margin calls if the value of their positions declines significantly, requiring additional funds to maintain the position.
- Short Squeeze: A rapid increase in the stock price can trigger a short squeeze, forcing traders to cover their positions at a loss.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations or market conditions can impact borrowing costs and affect the viability of short selling strategies.
Case Studies: Borrowing Costs in Action
Examining case studies of borrowing costs in action can provide valuable insights into how these costs can impact trading strategies and outcomes. For example, during the GameStop short squeeze in early 2021, borrowing costs for GME stock skyrocketed as demand for short selling surged. This led to significant challenges for traders, as they faced high expenses and increased risk exposure. By analyzing such cases, traders can learn from past experiences and develop more effective strategies for managing borrowing costs in the future.
How to Stay Updated on GME Stock Borrowing Costs?
Staying updated on GME stock borrowing costs is crucial for traders looking to make informed decisions. To do so, traders can:
- Monitor Financial News: Follow financial news sources for updates on market trends and changes in borrowing costs.
- Use Trading Platforms: Utilize trading platforms that provide real-time data on borrowing costs and other relevant metrics.
- Engage with Online Communities: Participate in online forums and communities where traders share insights and information on borrowing costs.
- Consult with Brokers: Regularly communicate with brokers to obtain the latest information on borrowing costs and market conditions.
Comparing Borrowing Costs Across Different Stocks
Comparing borrowing costs across different stocks can provide valuable insights into market dynamics and help traders identify opportunities for short selling. By analyzing the borrowing costs of various stocks, traders can assess the relative attractiveness of different short selling opportunities and make more informed decisions. Factors to consider when comparing borrowing costs include the stock's volatility, market demand for short selling, and the overall market environment.
What Tools Can Help Analyze Borrowing Costs?
Several tools can assist traders in analyzing borrowing costs and making informed decisions, including:
- Stock Screener Tools: Use stock screener tools to filter and compare borrowing costs across different stocks.
- Trading Platforms: Utilize trading platforms that provide real-time data on borrowing costs and other relevant metrics.
- Financial Analysis Software: Leverage financial analysis software to perform in-depth analysis of borrowing costs and their impact on trading strategies.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Employ data analytics platforms to identify trends and patterns in borrowing costs over time.
How to Predict Future Borrowing Costs?
Predicting future borrowing costs requires a thorough understanding of market dynamics and the factors that influence borrowing costs. Traders can use various methods to forecast future borrowing costs, such as:
- Technical Analysis: Analyze historical data and price patterns to identify trends that may indicate future changes in borrowing costs.
- Fundamental Analysis: Evaluate economic indicators, interest rates, and market conditions to assess their potential impact on borrowing costs.
- Sentiment Analysis: Monitor investor sentiment and market news to anticipate changes in demand for short selling and their effect on borrowing costs.
- Quantitative Models: Develop quantitative models to simulate different scenarios and predict potential changes in borrowing costs.
The Future of GME Stock Cost to Borrow
The future of GME stock cost to borrow will be shaped by a multitude of factors, including market conditions, regulatory changes, and investor sentiment. As the market continues to evolve, traders must remain vigilant and adapt their strategies to navigate the complex and dynamic landscape of borrowing costs. By staying informed and leveraging the latest tools and techniques, traders can effectively manage borrowing costs and capitalize on potential opportunities in the market.
Article Recommendations
- Is Michael Jackson Really Still Alive The Uncovering Truth
- All The Details On Waylon Jennings Children And Their Lives
- Pistol Pete Osu The Legacy Of A Basketball Legend